Implementation Status of Corporate Governance
Director Selection
The “Articles of Association” of our company stipulate a comprehensive candidate nomination system for the election of directors. The “Director Election Regulations” and “Corporate Governance Practices Guidelines” specify that the composition of the board of directors should consider diversification. In addition to possessing professional backgrounds and skills, consideration should also be given to the company’s future development, long-term strategic planning, and the diverse professional knowledge required by the company. The selection process for board members adheres to the principles of fairness, openness, and impartiality to select individuals with the necessary expertise, practical experience, and technical competencies to fulfill their duties as directors, thus achieving the ideal goal of corporate governance.
Execution Situation of the Company
In response to operational needs, the board of directors of our company is composed of nine members. In the framework of the company’s future development and long-term strategic planning, we seek suitable board members, whether general directors or independent directors, who are characterized by integrity, responsibility, innovation, and decision-making ability. Personality traits that align with the company’s core values, relevant industry experience, as well as factors such as gender and age balance, are considered in the selection process to form the best board of directors, promoting the company’s development and maximizing its interests.
Each director is required to complete at least 6 hours of continuing education annually during their tenure to assist them in continuously updating their knowledge and maintaining their core values and professional advantages and capabilities.
The company also stipulates the “Director Performance Evaluation Method.” An evaluation is conducted annually, measuring the effectiveness of the board through internal self-assessment and self-assessment by board members. This evaluation helps confirm the effectiveness of the board’s operations and assesses the performance of directors, serving as a reference for future director selection.
Succession Planning for Key Management Levels
- Employees at department head level (Grade 9) and above are considered key management personnel and potential successors. They are responsible for overseeing relevant business and operational management within the organization. Each management level has designated deputies to ensure continuity of duties. In addition to possessing the necessary professional skills and experience, key management personnel must align with the company’s corporate culture in terms of values and management philosophy. Their personal qualities must include integrity, vision, innovation, and the ability to earn the trust of both employees and customers.
- Through monthly participation in group management meetings, collective involvement in training and continuing education programs related to important operational decisions, and rotations, project assignments, and group ideology advocacy, we strengthen management capabilities, cultivate multifunctional and forward-thinking leadership, and enhance decision-making execution.
Execution Situation of the Company
- In July 2022, Manager Chen Ruisui from the Audit Department exchanged positions with Manager You Yajing from the Finance Department, with Manager Chen Ruisui assuming the responsibilities of the Finance Department and Manager You Yajing transferring to the Audit Department.
- In March 2023, Deputy Manager Chen Jinnong from the Management Department was transferred to Factory Two to oversee manufacturing management.
- In March 2023,Shipping Department Supervisor Lin Sukui concurrently assumed responsibilities in the Human Resources Department, overseeing employee education and training planning and student management. Through job rotations and training, we aim to develop future key management personnel and successors.
- In May 2024, Mr. Su Chieh-Liang and Mr. Lin Yu-Cheng were promoted to Assistant Vice Presidents of the Company. Their appointments aim to leverage their extensive industry experience to further enhance the Company’s operational effectiveness and maximize overall performance.
- In June 2025, Vice President Mr. Huang Kung-Long was promoted to the position of President (General Manager) of the Company.
The board of directors of our company completed the assessment of the independence of certified public accountants in the 114th year of the Republic, and obtained the declaration of absolute independence issued by the certified public accountants. The assessment results were reported to the Audit Committee and the Board of Directors for deliberation on February 25, 114th year of the Republic, and relevant assessment items are as detailed in 1-1.
In the 112th year of the Republic, the board of directors resolved to amend the ‘Corporate Governance Best Practices Guidelines’ and stipulated that regular (at least once a year) reference should be made to the Audit Quality Indicators (AQI) to assess the independence and suitability of appointed accountants. The results were reported to the Audit Committee and the Board of Directors for approval. The independence and suitability of the accountants appointed by the company were assessed based on the Audit Quality Indicators (AQI) by the board of directors’ unit of the company in the 113th year of the Republic. They all met the company’s standards of independence and suitability, qualified to serve as the company’s certified public accountants, and obtained the declaration of absolute independence issued by the certified public accountants. The assessment results were approved by the Audit Committee and the Board of Directors after deliberation on February 25, 114th year of the Republic, and the relevant assessment key items are listed as detailed in 1-2.
1-1 Auditor Independence Assessment Criteria
| Assessment Item | Yes | No |
| 1.Not an employee of the company or its affiliated enterprises. | v | |
| 2.Not a director or supervisor of the company or its affiliated enterprises (except for independent directors of the company, its parent company, or subsidiaries in which the company directly or indirectly holds more than 50% of the voting shares). | v | |
| 3.Not a natural person shareholder who, together with their spouse, minor children, or shares held under others' names, holds 1% or more of the total issued shares of the company or is among the top ten shareholders. | v | |
| 4.Not the spouse, a relative within the second degree of kinship, or a direct blood relative within the third degree of kinship of any person listed in the preceding three items. | v | |
| 5.Not a director, supervisor, or employee of a corporate shareholder that directly holds 5% or more of the company’s total issued shares, nor a director, supervisor, or employee of a corporate shareholder that is among the top five shareholders. | v | |
| 6.Not a director (trustee), supervisor, manager, or shareholder holding more than 5% of a specific company or institution that has financial or business dealings with the company. | v | |
| 7.Not married to or within the second degree of kinship with any other director. | v | |
| 8.Does not fall under any of the circumstances specified in Article 30 of the Company Act. | v | |
| 9.Not elected as a representative of a government agency, legal entity, or its representative as specified in Article 27 of the Company Act. | v | |
| 10.Has not served as a director, manager, or held a position with significant influence over audit matters in the company within the past two years. | v | |
| 11.Whether an "independence declaration" issued by the appointed accountant has been obtained. | v |
Work Performance and Effectiveness
| Assessment Item | Yes | No |
| 1.Timely completion of the company's periodic financial statements. | v | |
| 2.Timely completion of periodic financial audits for investment subsidiaries. | v | |
| 3.Providing financial and tax advisory services to the company on an as-needed basis. | v |
1-2 Auditor Independence and Suitability Assessment Criteria
| AQI Indicators | Focus of Measurement | Meeting the Criteria |
| Aspect One: Professionalism | ||
| (1-1) Audit Experience | Whether accountants and above-level audit personnel have sufficient audit experience to perform audit work. | Meeting the Criteria |
| (1-2) Training Hours | Whether accountants and above-level audit personnel receive sufficient education and training to continuously acquire professional knowledge and skills. | Meeting the Criteria |
| (1-3) Turnover Rate | Whether the firm maintains a sufficient number of senior human resources. | Meeting the Criteria |
| (1-4) Professional Support | Whether the firm has sufficient professional personnel (such as evaluators) to support the audit team. | Meeting the Criteria |
| Aspect Two: Quality Control | ||
| (2-1) Accountant Workload | Whether the accountant workload is excessive, including the number of public issuers supervised and the percentage of accountant working hours invested. | Meeting the Criteria |
| (2-2) Audit Input | Whether the investment of audit team members at each audit stage is appropriate. | Meeting the Criteria |
| EQCR Review Situation | Whether the accountant assigned to the Quality Control Review (EQCR) invests sufficient time to review the audit case. | Meeting the Criteria |
| Quality Control Support Capability | Whether the firm has sufficient quality control personnel to support the audit team. | Meeting the Criteria |
| Aspect Three: Independence | ||
| (3-1) Non-Audit Service Fees | The impact of the proportion of non-audit service fees on independence. | Meeting the Criteria |
| (3-2) Client Familiarity | The impact of the cumulative years of providing audit services for certified clients on independence. | Meeting the Criteria |
| Aspect Four: Supervision | ||
| (4-1) External Inspection Deficiencies and Penalties | Whether the firm's quality control and audit cases are executed in accordance with relevant laws and regulations and standards. | Meeting the Criteria |
| (4-2) Supervisory Authority's Letters for Improvement | Whether the firm's quality control and audit cases are executed in accordance with relevant laws and regulations and standards. | Meeting the Criteria |
| Aspect Five: Innovation Capability | ||
| (5-1) Innovative Planning and Advocacy | The commitment of the accounting firm to improve audit quality, including the innovative ability and planning of the accounting firm. | Meeting the Criteria |
Operation of Corporate Governance and Differences from the Practices Guidelines for Listed and Over-the-Counter Companies
1. Establishing Relevant Risk Management Policies or Strategies
The company formulated risk management measures in 2020, covering various risk management categories, organizational structures, assessment procedures, and risk management policy guidelines concerning external environments, economics, politics, laws, industries, and internal operations.
2. Establishing Appropriate Environmental Management Systems
The company’s subsidiaries’ production processes are certified through ISO 9000, ISO 14000, and IATF 16949, aiming to reduce environmental pollution during production. All management systems comply with environmental regulations. The company has internally developed environmental safety management operations, actively managing environmental and occupational health and safety aspects, ensuring employee workplace safety and health, and maintaining ecological balance.
3. Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Utilizing Environmentally Friendly Materials
The company and its subsidiaries will continue to research and develop low-pollution materials to replace those used in products and recycle production waste. Efforts are ongoing to improve energy efficiency, including paperless initiatives, energy-saving measures, waste reduction, and recycling, to minimize environmental impacts.
4. Potential Risks and Probabilities of Climate Change on Current and Future Business Operations
Periodic employee awareness programs on energy conservation and carbon reduction are conducted, with the company fully transitioning to LED lighting. Greenhouse gas reduction issues are incorporated into risk management processes, continually assessing the potential risks and opportunities of climate change, actively promoting energy conservation, carbon reduction, greenhouse gas reduction, water conservation, and other waste management plans.
5. Policies for Greenhouse Gas Reduction, Water Conservation, and Other Waste Management
Our company places great emphasis on energy conservation and carbon reduction, regularly educating employees on related practices. Reduction targets have been established, including the adoption of energy-saving products such as LED lighting and the continued promotion of electronic forms. In 2023, we successfully reduced per capita emissions by 1%, and in 2024, we aim to achieve a 9% reduction in total emissions.
Additionally, we have implemented a water conservation management plan with a five-year efficiency goal, targeting an annual water-saving rate of 1%. We are also committed to reducing overall industrial waste while increasing recyclable waste resources. The company carefully selects waste disposal and recycling service providers to ensure proper waste reduction and reuse, minimizing environmental risks.
6. Formulating Management Policies and Procedures in Accordance with Relevant Regulations and International Human Rights Conventions
The company adheres to relevant labor laws and international human rights conventions, formulating “work rules” and “salary cycles” to protect employees’ legal rights and interests. By complying with national laws, including labor standards, employment services, and gender equality laws, the company promotes internal work rule advocacy and provides complaint channels to maintain employee rights, ensuring fair treatment and respect for all employees. No instances of child labor, forced labor, or human rights violations have occurred.
7. Implementing Reasonable Employee Welfare Measures Reflecting Business Performance in Employee Salaries
The company implements humane management and various welfare measures, allocating 2% to 10% of profits as employee compensation in accordance with the company’s articles of association, proposed by the board of directors in the form of stock or cash dividends. Reasonable employee welfare measures are established and implemented, including salaries, vacations, and other benefits, with business performance appropriately reflected in employee salaries through salary compensation committee oversight, performance assessments, and bonus distributions.
8. Providing Employees with Safe and Healthy Work Environments
Regular employee health checks and a safe working environment are provided, with fire prevention and disaster preparedness training conducted to safeguard employee lives. Providing a safe, healthy, and comfortable working environment is a goal, promoting health and safety management to instill correct concepts and maintain physical and mental health among employees. This year, there were no work-related accidents among employees, with a 0% rate of work-related accidents occurring during commutes, and motorcycle safety promotion activities were conducted for affected employees.
9. Establishing Effective Career Development and Training Plans for Employees
To enhance employee skills and organizational competitiveness, internal education and training programs are developed, encouraging employees to participate in internal and external training courses. Employees are encouraged to improve themselves by participating in training courses related to different career capabilities, enhancing their professional skills, achieving career development goals, and ultimately achieving corporate operational objectives.
10. Formulating Policies to Protect Consumer or Customer Rights and Complaint Procedures
While the company does not sell products to end consumers, communication channels with customers are kept open, actively meeting customer requirements to continually improve customer satisfaction. Contact channels are established on the company’s website for direct communication with stakeholders. Marketing and labeling of products and services follow local regulations and international standards for customer and supplier rights.
11. Establishing Supplier Management Policies
The company formulates relevant articles such as subcontracting management methods and occupational safety and health management regulations. If a supplier’s contract violates its corporate social responsibility policy and significantly affects the environment and society negatively, the company reserves the right to terminate or dissolve the contract at any time, raising awareness among suppliers about social responsibility and environmental importance and observing their actual operational conditions.
12. ESG Implementation Status
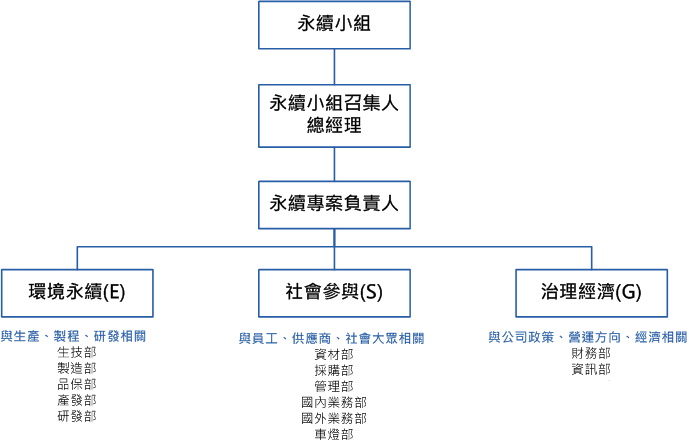
According to the schedule outlined in the roadmap for sustainable development of listed companies, our company, with a paid-in capital of less than 2 billion NT dollars, is required to submit the individual company sustainability report for the fiscal year 2024 by the end of August 2025. Progress on quarterly completion shall be reported to the Board of Directors.
2024 Sustainability Report Main Schedule Progress Table
| Work Items | Projected Execution Dates | Actual Execution Dates | Progress Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial meeting for Sustainable Report Guidance | December 2023 | December 4, 2023 | Completed |
| Sustainable Report Guidance - Education and Training Course - First session (Introduction to GRI 1 and GRI 2) | December 2023 | December 15, 2023 | Completed |
| Sustainable Report Guidance - Education and Training Course - Second session (Identification of stakeholders and significant topics in GRI 3) | December 2023 | December 22, 2023 | Completed |
| Planning the outline of the Sustainable Report | February 2024 | March 4,2024 | Completed |
| Identifying significant topics and reporting to the Board | February 2024 | March 12,2024 | Completed |
| Collection of relevant data for significant topics in the Sustainable Report in accordance with the "Operation Regulations for the Preparation and Declaration of Sustainable Reports by Listed Companies" | April to December 2024 to January 2025 | January 20,2025 | Completed |
| Drafting the initial version of the Sustainable Report | March to April 2025 | April 30,2025 | Completed |
| Finalizing the Sustainable Report | May 2025 | In Progress | |
| Graphic design for the Sustainable Report (approximately 1 to 1.5 months) | June 2025 | ||
| Finalizing the Sustainable Report after graphic design | End of August 2025 |
The 2024 Information Security Implementation Report was presented to the Board of Directors on December 24, 2024.
1. Scope of Application
Matters concerning information security shall be handled in accordance with these regulations unless otherwise specified.
2. Information Security Organizational Management Framework
To implement information security management, the company shall establish an information security organization, which shall include senior executives of the company, responsible for promoting, coordinating, and supervising the following information security management matters:
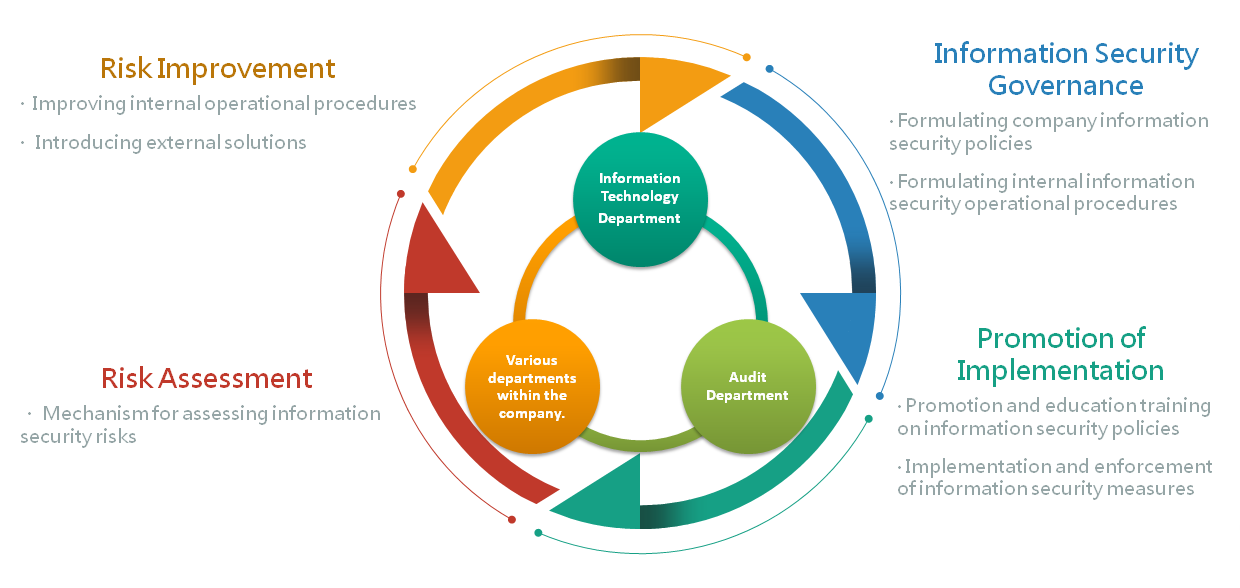
- Approval and supervision of information security policies.
- Allocation and coordination of information security responsibilities.
- Supervision of information asset protection matters.
- Review and supervision of information security incidents.
- Approval of other information security matters.
3. Account Management
- Information systems must have account and password login management functions.
- Depending on the business functions, account types shall be distinguished, with each employee using one set of account and password for each type. Users must properly safeguard their personal accounts and passwords, with passwords being at least six characters long and changed every three months. Personal passwords must be kept strictly confidential, and if leakage is detected, they must be changed immediately to ensure information security.
- Upon changes in personnel, accounts and permissions shall be disabled or deleted according to their status, as approved by the responsible supervisor.
4. Data Access
- Network monitoring systems shall be installed to monitor communication lines, protocols, data traffic, data content, and usage objects, managed by designated personnel from the information department.
- Important servers shall be installed within the company’s protected network, with internal and external networks separated by security devices (firewalls) and security access permissions set according to business needs.
- Requests for changes in firewall security permissions shall be modified by designated personnel upon approval from the information department, with the change history recorded.
- The information department shall periodically review firewall security permissions and computer network security matters, and establish a network intrusion detection system to effectively detect malicious intrusion events.
- When transmitting confidential data via public networks, data encryption mechanisms shall be employed.
- Firewall system software shall be regularly updated to address various network attacks.
5. Network Security Management
- Network monitoring systems shall be installed to monitor communication lines, protocols, data traffic, data content, and usage objects, managed by designated personnel from the information department.
- Important servers shall be installed within the company’s protected network, with internal and external networks separated by security devices (firewalls) and security access permissions set according to business needs.
- Requests for changes in firewall security permissions shall be modified by designated personnel upon approval from the information department, with the change history recorded.
- The information department shall periodically review firewall security permissions and computer network security matters, and establish a network intrusion detection system to effectively detect malicious intrusion events.
- When transmitting confidential data via public networks, data encryption mechanisms shall be employed.
- Firewall system software shall be regularly updated to address various network attacks.
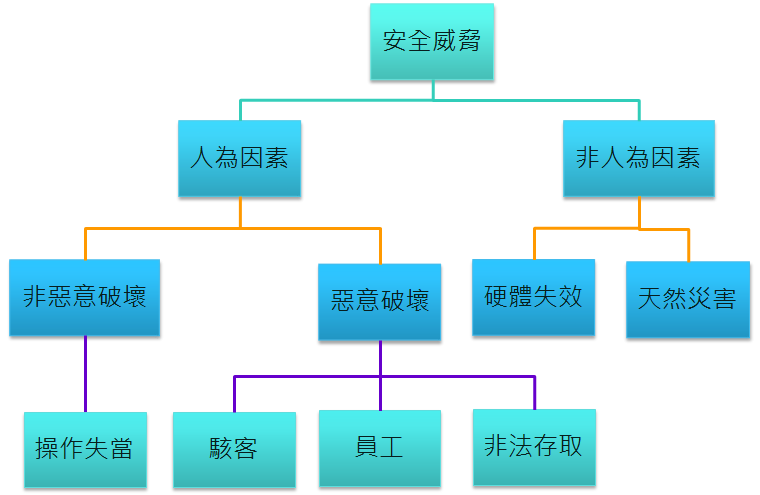
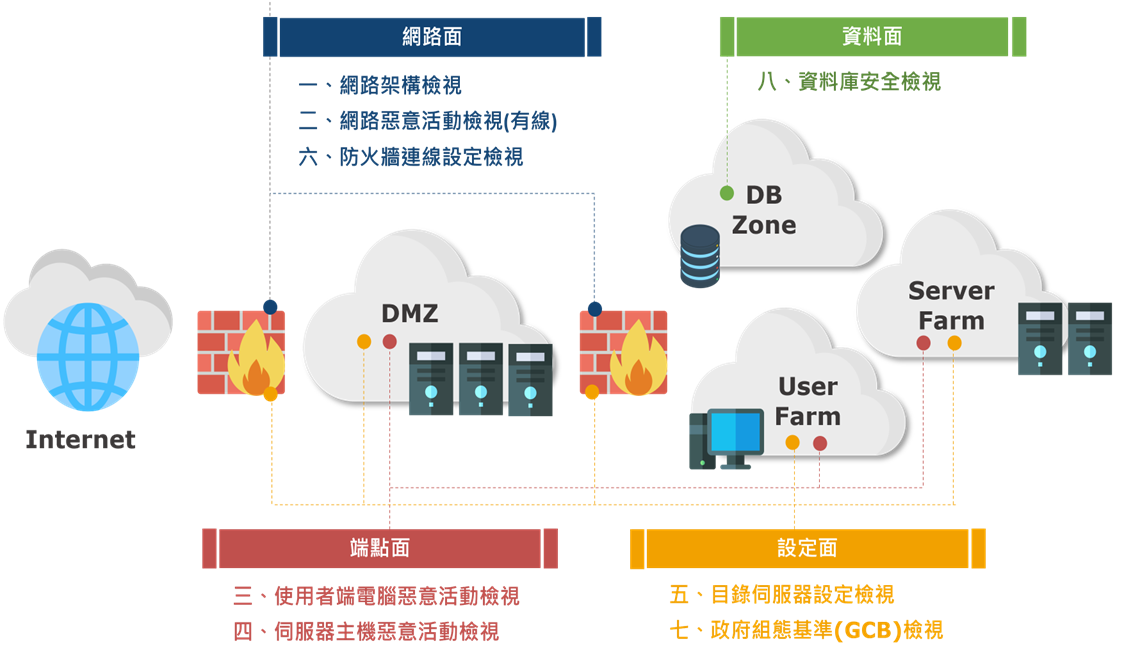
6. Information Security Policies and Management Practices
Risk Management
In recent years, global enterprises have faced significant changes in the economic environment, such as trade controls between China and the United States, disruptions caused by emerging high technologies in cybersecurity, and the spread of the Covid-19 virus. These issues have led to substantial losses for companies due to inadequate responses. Some industries, such as aviation, automotive, and tourism, have even been forced to cease operations.
To avoid potential risks that may lead to operational crises and in line with the spirit of sustainable operations, Shian Yih established a risk management organization in 2020. It formulated risk management methods and procedures to effectively monitor and reduce losses caused by risks, allowing the company to continue its operations within an acceptable risk range and achieve its business goals.
Risk management covers various external risks such as environmental, economic, political, legal, technological, and industry-related factors, as well as internal operational risks such as operational security, quality, information security, occupational health and safety, and financial risks. In addition to existing management functions and institutional regulations, cross-departmental organizations such as project teams and risk management groups are established to effectively supervise and manage risks based on the type of risk.
Types of Risks and Management Scope
| Risk Types | Considerations | Risk Explanations | Functional (Responsibility) Units |
| External Risks | Environmental, political, economic, legal, technological, and industrial changes |
|
Finance Department, General Manager/Board of Directors, Sales Department, Production Development Department, Research and Development Department, etc. |
| Internal Operational Risks | Sales |
|
Sales Department |
| Production cycle |
|
Manufacturing Department, Quality Assurance Department, Biotechnology Department, Plant Management, Production Management (Materials) | |
| Supply chain |
|
Procurement Department | |
| Information security |
|
Information Technology Department | |
| Human resources |
|
Management Department (Human Resources) | |
| Environmental and operational safety |
|
Management Department | |
| Legal compliance |
|
Management Department, Intellectual Property Team | |
| Intellectual property |
|
Intellectual Property Team | |
| Internal control |
|
Entire company, Audit Department | |
| Financial Risks | Financial |
|
Finance Department |
| Investment |
|
Finance Department | |
| Others | Other risks not mentioned above |
|
Establishment of risk project teams |
Note: The functional units (responsibility units) for managing various types of risks may change depending on practical circumstances, organizational adjustments, and appointments by the highest risk authority.
Risk Management Organizational Structure
The implementation of risk management-related operations will be carried out by relevant units and personnel based on the sources and types of risks. In addition to following existing management structures and internal control systems, unit managers will collaborate with other units according to assigned project responsibilities. The planning department is responsible for summarizing the risk management situation and reporting upwards within the authority.
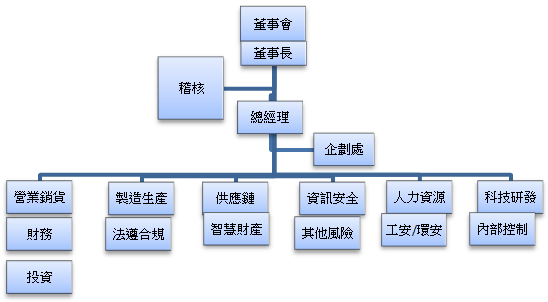
| Types of risks | Risk identification | Risk control measures |
| External risks | Tariff regulations on Sino-US trade |
|
| Internal operations | Financial |
|
| Supply chain |
|
|
| Product quality |
|
|
| Occupational health and safety |
|
|
| Digital information security |
|
|
| Others | Counter-terrorism and customs cargo security |
|
The risk management procedures were approved by the board of directors on December 23, 2020. Starting from 2021, the report will be presented at the last board meeting each year. The latest risk management report was completed and presented to the board on December 24, 2024. For detailed report content, please click the link below to download.
Report on the Implementation of Integrity Management for Year 113
Submitted to the Board of Directors on November 7, Year 113
1. Regulations
According to Article 5 (Dedicated Unit) of the company’s “Procedures for Integrity Management and Code of Conduct,” the implementation of corporate integrity management should be reported to the Board of Directors periodically (at least once a year):
- Assisting in integrating integrity and ethical values into the company’s business strategy and formulating compliance measures to ensure integrity management.
- Promoting and coordinating the implementation of integrity policy advocacy and training.
- Planning a whistleblower system to ensure effective implementation.
- Assisting the Board of Directors and management in reviewing and assessing the effectiveness of preventive measures for integrity management and regularly evaluating compliance within business processes to compile reports.
2. Implementation Results
As of October 18, Year 113, no incidents violating integrity management policies have been identified, and no internal or external whistleblower reports or legal cases related to integrity management have been received. Therefore, the company has not violated the corporate integrity management guidelines in Year 113.
The following is a report on the assessment items and implementation results:
| Evaluation Items | Operational Status | Differences from the Ethical Corporate Management Best Practice Principles for Listed Companies and Reasons |
| Summary Description | ||
|
1.Establishment of Integrity Management Policies and Programs (a) Has the company established an integrity management policy approved by the Board of Directors and clearly stated it in regulations and external documents, along with commitments from the Board and senior management to actively implement the policy? (b) Has the company set up a risk assessment mechanism for dishonest behavior, periodically analyzing and evaluating business activities with higher risks of dishonest behavior, and formulated preventive measures in accordance with Article 7, Section 2 of the "Listed Companies Integrity Management Guidelines"? (c) Does the company clearly define operational procedures, codes of conduct, disciplinary actions, and appeal mechanisms in its dishonest behavior prevention program and regularly review and revise the program? |
A. To demonstrate the company's commitment to social and environmental responsibility and adherence to corporate ethical standards, the company has established the "Procedures for Integrity Management and Code of Conduct," "Code of Ethical Conduct," and "Work Rules." These regulations stipulate that Board members, employees, and subsidiaries must avoid conflicts of interest, comply with legal regulations, strictly maintain business confidentiality, and report any illegal or unethical behavior. B. The "Procedures for Integrity Management and Code of Conduct" and "Code of Ethical Conduct" were revised on June 12, Year 112, and implemented after approval by the shareholders' meeting. All employees must adhere to these guidelines, and any corruption or fraud will be handled in accordance with relevant policies. C. All employees have signed the "Statement of Compliance with Integrity Management Policies," ensuring full compliance. New employees are informed of the company’s regulations upon onboarding and must sign the statement as part of their training. Violations result in disciplinary action, including contract termination for severe cases. |
No major discrepancies. |
|
2. Implementation of Integrity Management (a) Does the company assess the integrity records of counterparties and include integrity clauses in contracts with business partners? (b) Has the company established a dedicated (or concurrent) unit under the Board of Directors to promote corporate integrity management and regularly (at least once a year) report to the Board on its integrity management policy, prevention measures, and supervision of implementation? (c) Has the company formulated conflict-of-interest prevention policies and provided appropriate reporting channels for implementation? (d) Has the company established effective accounting and internal control systems to ensure integrity management? Are internal audit units responsible for conducting audits based on the assessment of dishonest behavior risks, or are external accountants commissioned for verification? (e) Does the company regularly conduct internal and external training on integrity management? |
A. The company evaluates business partners' legality, integrity management policies, and past records of dishonest behavior before establishing commercial relationships to ensure fair, transparent business practices. B. The company's Management Department is responsible for promoting integrity management and reports at least once a year to the Board, with the latest report presented on November 7, Year 113. The implementation status for Year 113 is disclosed on the company's website. C. Directors adhere to high self-discipline standards, abstaining from discussions and voting on matters where conflicts of interest may arise. Employees must report potential conflicts of interest to their supervisors and the dedicated unit. D. An internal control system is in place, with annual reviews and revisions conducted by audit personnel to ensure effective corporate governance and risk control. E. Integrity management training is integrated into new employee onboarding, and periodic training is conducted for all employees.
|
No major discrepancies. |
|
3. Whistleblower System Operations (a) Has the company established specific whistleblower and reward mechanisms with accessible reporting channels and assigned responsible personnel to handle reports? (b) Has the company established standard operating procedures for handling whistleblower reports, follow-up measures, and confidentiality mechanisms? (c) Does the company have measures to protect whistleblowers from unfair treatment? |
A. The company has both internal and external whistleblower systems to report any illegal or unethical activities. A dedicated independent unit conducts investigations, ensuring strict confidentiality. Reports can be submitted via email (shianyih8020@gmail.com) or phone (04-23590111 #8020, Ms. You). B. Whistleblower identities are strictly confidential to prevent unfair treatment.
|
No major discrepancies. |
|
4. Strengthening Information Disclosure (a) Does the company disclose its integrity management guidelines and implementation effectiveness on its website and the public information observatory? |
A. The company maintains a website that provides company information and updates related announcements on the public information observatory. |
No major discrepancies. |
|
5. Compliance with Listed Companies Integrity Management Guidelines The company established the "Procedures for Integrity Management and Code of Conduct" on December 22, Year 100, and revised it in June, Year 111. The overall implementation aligns with the "Listed Companies Integrity Management Guidelines."
|
||
|
6. Other Key Information on Integrity Management (a) The "Board of Directors Meeting Rules" includes conflict-of-interest avoidance policies for directors. (b) The company has established "Insider Trading Prevention Management" and "Internal Material Information Handling Procedures" to regulate disclosure and confidentiality of significant company information. (c) The company’s integrity management policies aim to build a transparent and responsible corporate governance system. (d) Internal control measures are designed to mitigate corruption risks, with regular assessments and reports to the Audit Committee and Board of Directors. (e) Further details on the company’s integrity management can be found on the ESG section of the company website.
|
||
3. Education and Training
- New employees sign a “Statement of Compliance with Integrity Management Policies” upon onboarding. In 2024, 100% of new hires signed the statement.
- In-service employees (including directors and senior managers) undergo periodic online and in-person integrity management training sessions.
4. Integrity Management Plan for Year 2025
- Continuously revise integrity management policies and related regulations in compliance with laws.
- Continue training on “Insider Trading Prevention,” “Procedures for Integrity Management and Code of Conduct,” and “Code of Ethical Conduct” for directors, managers, and employees.
- Regularly audit internal and external whistleblower reports and investigate cases of dishonesty or unethical behavior following company policies and internal control procedures.
- Submit a Sustainability Report in 2025, supervised by the Sustainability Task Force, to reinforce corporate integrity culture and extend ethical management standards to suppliers and stakeholders.
Our company has established the ‘Internal Procedures for Handling Material Information’ and the ‘Measures for Preventing Insider Trading’ to prohibit insiders from trading securities based on undisclosed information in the market. These serve as the basis for our significant information processing and disclosure mechanisms, and are publicly available on our company’s website for reference. We also conduct periodic reviews of these regulations to ensure compliance with current laws and practical management needs.
Implementation of Insider Trading Prevention Measures:
1. Our company conducts annual education and promotion on the ‘Measures for Preventing Insider Trading’ and relevant regulations for current internal personnel and related colleagues. Additionally, newly appointed internal personnel receive a company-prepared briefing upon assuming their positions, covering various regulations and points of attention to facilitate compliance.
2. Starting from the third quarter of 2022, our company has conducted briefings on the provisions of Article 157-1 of the Securities and Exchange Act before the announcement of quarterly operating results, targeting internal personnel, specific position supervisors, and colleagues. The content includes reminders about the quiet period, the scope and subjects prohibited from insider trading, the scope of information that may significantly impact stock prices and its disclosure methods, penalties, and legal provisions. Internal personnel (including but not limited to the board of directors) are required not to trade company stocks during the 30-day period before the announcement of annual financial reports and the 15-day period before the announcement of quarterly financial reports, to effectively prevent insider trading.
| Financial Reporting Period | Board Meeting and Announcement Date | Notification | Prohibition of Trading Insider Stocks (Closed Period) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 Q3 Financial Report | 2022/11/10 | 2022/10/17 | 2022/10/21-2022/11/9 |
| 2022 Financial Report | 2023/3/15 | 2023/2/7 | 2023/2/13-2023/3/16 |
| 2023 Q1 Financial Report | 2023/5/11 | 2023/4/24 | 2023/4/26-2023/5/12 |
| 2023 Q2 Financial Report | 2023/8/10 | 2023/7/24 | 2023/7/26-2023/8/11 |
| 2023 Q3 Financial Report | 2023/11/9 | 2023/10/20 | 2023/10/26-2023/11/10 |
| 2023 Financial Report | 2023/3/12 | 2023/1/31 | 2022/2/7-2023/3/13 |
| 2024 Q1 Financial Report | 2024/5/9 | 2024/4/18 | 2024/4/22-2024/5/10 |
| 2024 Q2 Financial Report | 2024/8/8 | 2024/7/18 | 2024/7/22-2024/8/9 |
| 2024 Q3 Financial Report | 2024/11/7 | 2024/10/15 | 2024/10/21-2024/11/8 |
| 2024 Financial Report | 2025/2/25 | 2025/1/16 | 2025/1/20-2025/2/26 |
3. Periodically, through email or notification letters, directors and internal personnel are informed to relay to the Taiwan Stock Exchange Corporation the template for ‘Violation of Securities and Exchange Act Regulations Regarding Insider Trading Reporting of Shareholding Changes by Insiders.’ It is also reminded that when benefiting from short-term trading activities, the company reserves the right to request internal personnel to attribute such gains to the company.
4. Starting from May 2023, our company has conducted online educational briefings for new employees upon their onboarding. Additionally, before each employee training session, we present a briefing on “Insider Trading and Related Regulations for Insiders” in the form of a slideshow. A test is administered after the briefing, and the results indicate that the educational efforts have been effective.
To strengthen technological growth and competitive advantage, our company has positioned its intellectual property (IP) strategy with the goal of enhancing “patent quality” rather than focusing solely on “patent quantity.” We integrate our company’s focus on technology and products with patents, aiming to create industry value and increase revenue. Additionally, in accordance with corporate governance principles and evaluation indicators, we have developed an IP management system that integrates with our operational goals and technology development strategies.
Objectives of Intellectual Property Management:
- At least one patent proposal in the planned technical field will be completed in 2024.
- In 2024, the system will be completed and all trade secret documents will be archived in the internal management system within the set timeframe for tracking and inquiry.
- On November 21, 2024, a “Trade Secrets and Personal Data Protection Legal Seminar” will be held
- Achieve a 100% compliance rate for new employees in terms of understanding and signing obligations related to IP and trade secrets.
Intellectual Property Management Policy:
- Adhere to corporate governance regulations to implement IP management effectively.
- Strengthen key technologies internally and comprehensively deploy intellectual property.
- Protect and utilize research and development achievements, enhancing trade secret protection.
- Enhance employee awareness of IP to create IP value.
Our company executed the Intellectual Property Management Plan and reported it to the board of directors on December 24, 2024. To ensure compliance with corporate governance regulations and to link IP plans with operational objectives, the IP plan and annual execution status were disclosed on the company’s official website by December 30, 2024.
Intellectual Property Inventory and Results:
| Intellectual Property Classification | Patent application in progress | Patent approved |
|---|---|---|
| Patent application in progress | 4 | |
| Patent application in progress | 1 | 3 |
| Patent application in progress | 2 | |
| Patent application in progress | 14 |
Trade Secret Document Inventory (2024/1/1~2024/11/30)
| Classification | Quantity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| New Employees | 4 | |
| Customers | 6 | |
| Supply Chain | 2 |
Contribution of Intellectual Property Rights to Corporate Operations:
1. Enhancement of IP Energy:
Patented technology is an important intangible asset for our company. We offer internal proposals and external application incentive measures annually to encourage R&D staff to protect their research results. Through an internal review mechanism for proposal applications, we can flexibly adjust patent application categories and countries based on the proposal’s technology, application aspects, and market trends to maximize the utility of patent protection.
2. Deepening Employee Awareness of IP:
We actively promote IP protection awareness to all employees through education and training sessions and internal seminars. Only when all staff members share the same awareness can we avoid unintentional infringement of others’ or the company’s IP rights, leading to litigation and impacting the company’s finances.
We regularly participate in and organize patent technology seminars to provide employees with guidelines for handling patent-related risks appropriately.
3. Achieving Sustainable Business Goals:
Each year, we conduct education and training for new and existing employees to promote an understanding of the importance of IP rights. We hope that all employees will work together to protect the company’s intellectual property, thereby achieving our corporate sustainability goals.
Intellectual Property Rights Risks and Countermeasures:
Shian Yih is facing changes in the LED backlight module market and technology. The company has gradually transformed and is actively developing new products and technologies along the upstream and downstream. Internally, various intellectual property management systems have been established. When developing technologies, the company faces intellectual property disputes and litigation, and always prioritizes protecting its market, products, technologies, and customers. For example, the company focuses on independently obtaining patents for core products as a primary goal. If necessary, the company will also collaborate externally and acquire patents. When encountering risks, the company has established a dispute resolution mechanism internally, analyzing technical, legal, and industrial aspects to devise dispute resolution strategies. It employs different approaches, such as creating technological entry barriers for competitors or avoiding infringing on others’ patents, while considering all factors comprehensively.
